In the year leading up to March, prices in the UK increased by 2.6%, which is lower than the prior month’s rise yet remains above the Bank of England’s targeted figure.
The Bank of England adjusts interest rates to aim for an inflation rate of 2%, and in 2025, it reduced them twice, bringing the rates down to 4.25%.
Earlier, the Bank had cautioned that it anticipated inflation would climb once more in 2025.
What is inflation?
Inflation refers to the rise in the cost of goods and services over a period of time.
If a bottle of milk priced at £1 increases to £1.05 after one year, the yearly milk inflation would be 5%.
What method is used to measure the inflation rate in the UK?
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) monitors the costs of numerous daily necessities such as food and fuel.
This digital “assortment of items” is frequently revised to mirror consumer preferences, with
VR headsets and yoga mats included in 2025
, with local newspaper advertisements taken out.

The ONS tracks price variations over the past year to determine inflation rates.
The primary inflation indicator is known as
the Consumers Price Index (CPI)
, with the most recent statistic released monthly.
CPI was
2.6% for the year ending March 2025
, decreasing to 2.8% for the 12-month period ending in February.
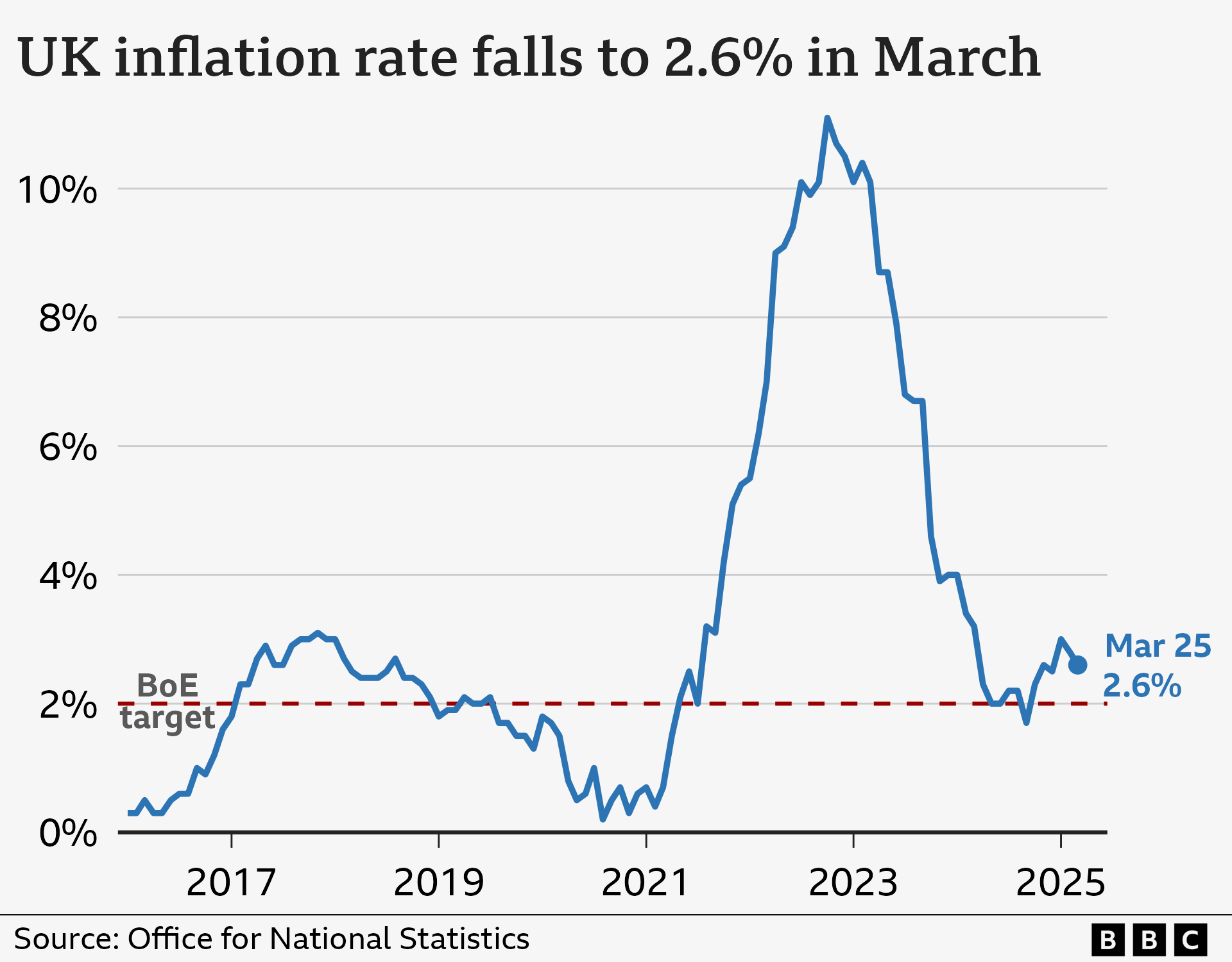
The decline was more significant than what financial experts anticipated, according to the ONS, primarily due to decreased costs for apparel and footwear.
The bank additionally takes into account metrics like “core inflation” when determining if and how to adjust interest rates.
The core Consumer Price Index excludes food and energy prices since these categories often exhibit significant volatility. Thus, it serves as a more reliable indicator of underlying long-term inflation trends.
This figure stood at 3.4% in March, marginally lower than the 3.5% recorded in February.
What factors are causing prices to continue increasing?
Inflation has dropped considerably after reaching 11.1% in October 2022, marking the peak level over four decades.
That said, this does not indicate a decrease in prices; rather, it suggests that price increases are slowing down.
In 2022, inflation rose sharply as oil and natural gas experienced increased demand following the COVID-19 pandemic. Energy costs escalated further when Russia’s invasion of Ukraine disrupted global markets.
It stayed significantly above the 2% target largely due to increased food costs.
How does increasing interest rates aid in reducing inflation?
As inflation remained significantly higher than its 2% objective, the Bank of England raised interest rates to 5.25%, which marked a 16-year peak.
The concept revolves around making borrowing costlier so that individuals have reduced funds available for spending. Additionally, this could motivate people to increase their savings.
Consequently, this leads to decreased demand for products and curbs inflation.
However, it’s a delicate balance — raising borrowing costs could potentially damage the economy.
For instance, homeowners may encounter increased mortgage payments, potentially offsetting more favorable saving offers.
Companies tend to take out fewer loans, reducing their likelihood of generating new employment opportunities. Others might lay off workers and decrease investments.
What’s occurring with the interest rates in the UK, and is another decrease likely?
The Bank of England reduced interest rates in August and November 2024, followed by further reductions in February and May 2025.
taking rates to 4.25%
.
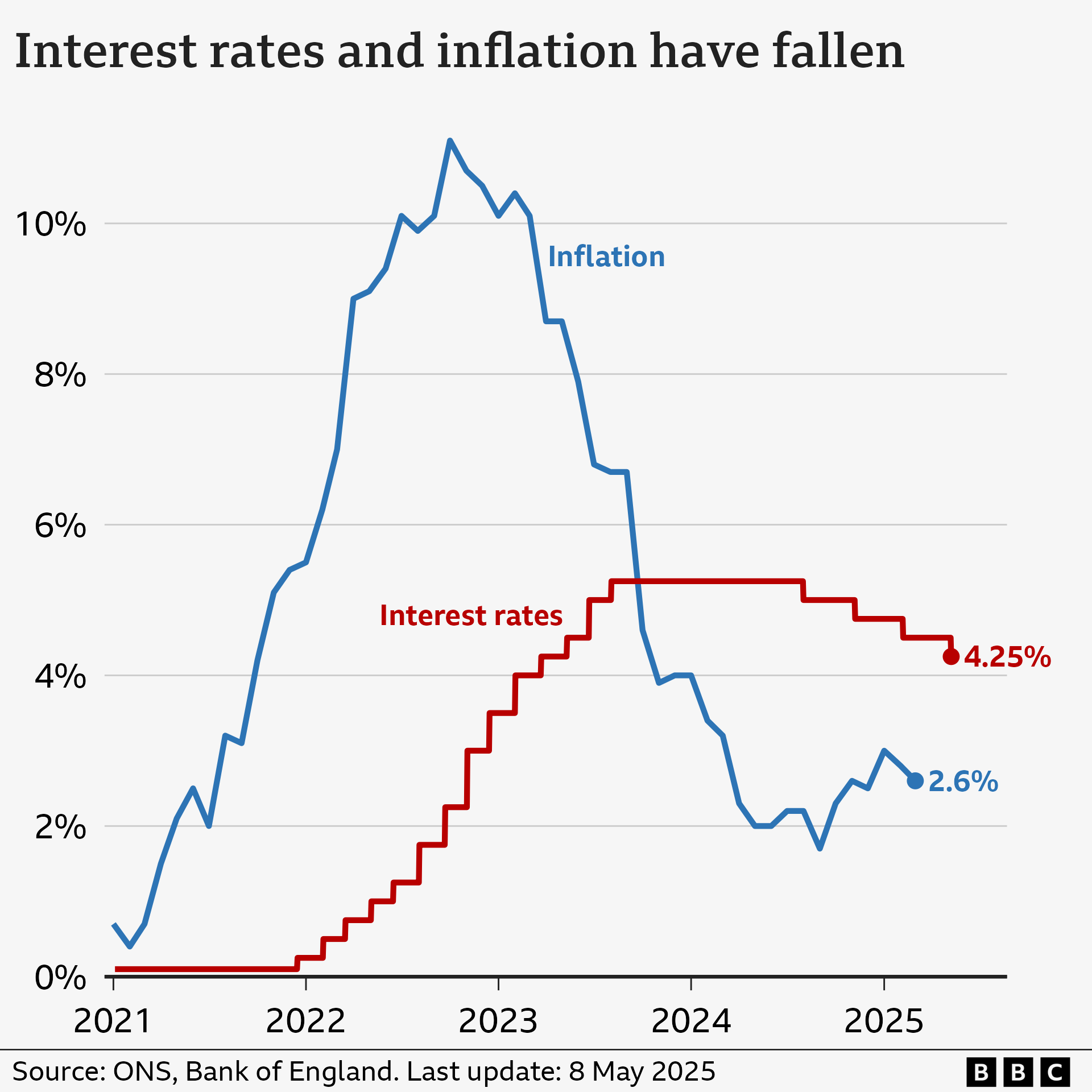
The Bank of England governor, Andrew Bailey, stated that the decision made in May was due to the decrease in inflation. He also suggested that additional “gradual and measured” reductions might take place subsequently.
However he warned that
the implementation of American trade duties
has demonstrated “the unpredictability of the global economy.” The Bank stated it anticipated that the tariffs would hinder the UK’s economic growth and result in lower inflation than projected.
Earlier, the Bank had indicated that it anticipated inflation to rise to 3.7% from July through September in 2025, then decrease again by late 2027.
- When can we expect interest rates to decrease once more?
- How Trump’s Tariffs Could Impact You and Your Finances
Is pay staying abreast of price increases?
The
latest official figures
demonstrate that regular wages in Great Britain
increased at a rate higher than inflation from December to February
.
The average yearly increase in compensation (not including bonuses) for the three-month period came out to be 5.9%.
When adjusted for inflation, salaries increased by 3% from December to February.
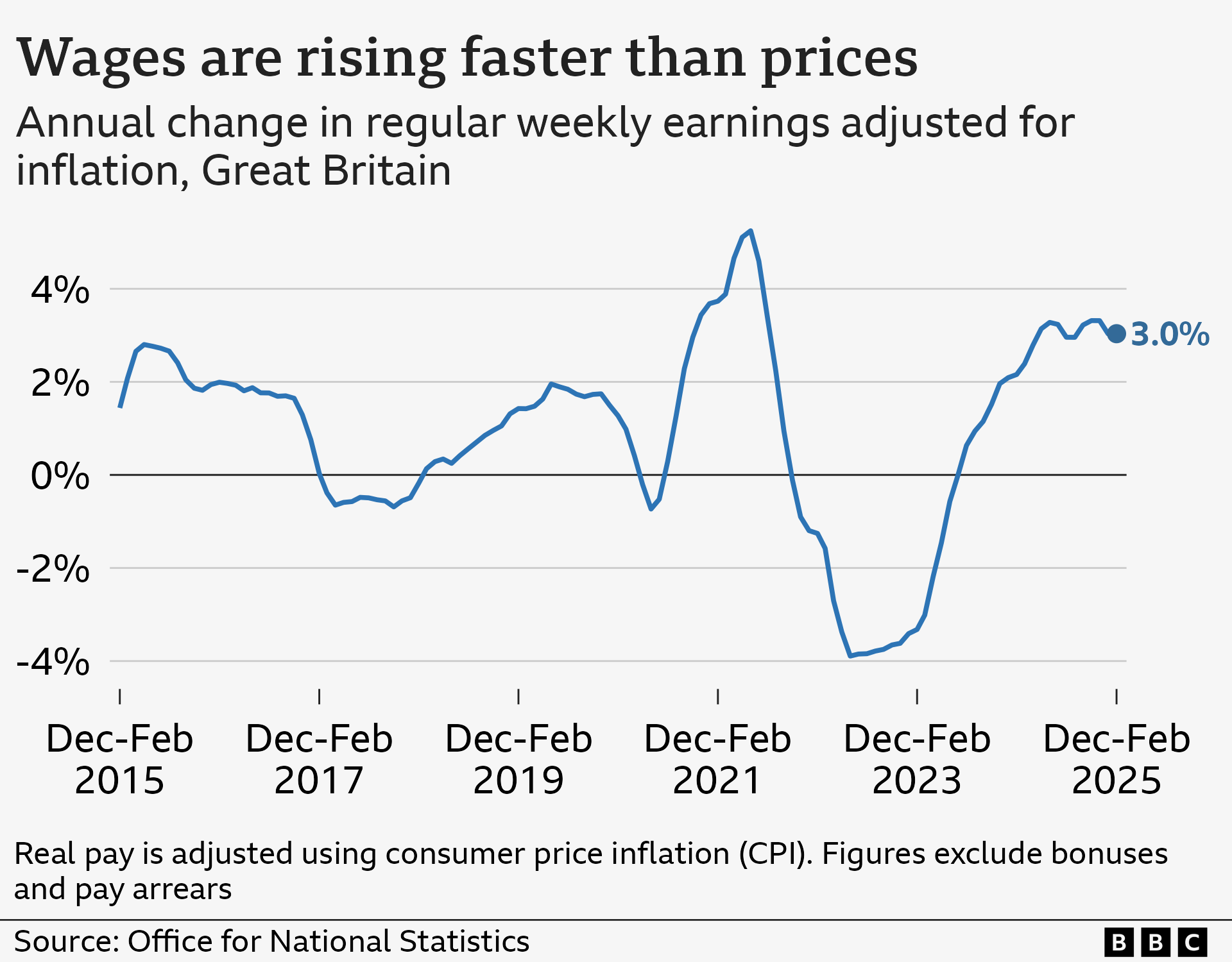
Earnings in the private sector grew at a faster rate than compensation in the public sector.
- Five suggestions for requesting a salary increase
- How to Secure Employment: Six Professional Tips for Job Hunting
- Who comprises the millions of British individuals who are unemployed?
What’s occurring with inflation and interest rates in Europe and the United States?
Both the United States and European Union nations have been attempting to curb rising prices.
In April 2025, the inflation rate for Eurozone countries stood at 2.2%, unchanged from March but marginally lower than the 2.3% recorded in February.
In June 2024, the European Central Bank (ECB) reduced its key interest rate from a record-high of 4% down to 3.75%, marking the first decrease after five consecutive years without change.
It has subsequently reduced rates an additional five times, bringing its benchmark rate down to 2.5%.
The inflation rate in the United States dropped to 2.4% in March, a decrease from February’s figure of 2.8%, yet it remains higher than the Federal Reserve’s targeted rate of 2%.
Following several reductions in late 2024, the U.S. central bank decided to keep interest rates steady during its May meeting, pointing to the ambiguity created by
the US tariffs
.
This keeps their main interest rate steady between 4.25% and 4.5%.
The Federal Reserve has
frequently face attacks from President Trump
, who want to see additional reductions.


Leave a Reply